For Customizing Records¶
In this section, we will cover the following functions in-depth listed below:
uadmin.Delete¶
func Delete(a interface{}) (err error)
Delete records from database.
Parameter:
a interface{}: Is the variable where the model was initialized
Before we proceed to the examples, read Tutorial Part 9 - Introduction to API to familiarize how API works in uAdmin.
- Example #1: By Using API Handler (uadmin.Delete)
- Example #2: By Drop Down List Selection (uadmin.Delete)
Example #1: By Using API Handler (uadmin.Delete)¶
Suppose you have five records in your Todo model.
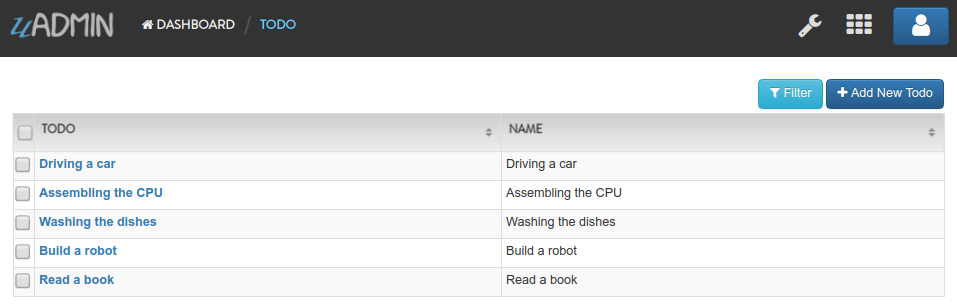
Create a file named delete.go inside the api folder with the following codes below:
// DeleteHandler !
func DeleteHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// r.URL.Path creates a new path called "/delete/"
r.URL.Path = strings.TrimPrefix(r.URL.Path, "/delete")
r.URL.Path = strings.TrimSuffix(r.URL.Path, "/")
// Initialize the Todo model
todo := []models.Todo{}
// Delete all records in Todo model
uadmin.Delete(&todo)
}
Establish a connection in the main.go to the API by using http.HandleFunc. It should be placed after the uadmin.Register and before the StartServer.
func main() {
// Some codes
// DeleteHandler
http.HandleFunc("/delete/", uadmin.Handler(api.DeleteHandler)) // <-- place it here
}
api is the folder name while DeleteHandler is the name of the function inside delete.go.
Run your application. Add /delete/ path after your access IP and port in the address bar (e.g. http://0.0.0.0:8080/delete/).
Afterwards, go to Todo model and see what happens.
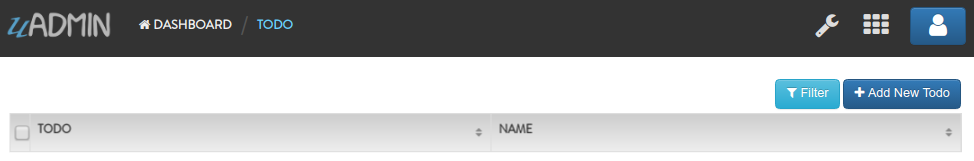
All records are deleted from the database.
Example #2: By Drop Down List Selection (uadmin.Delete)¶
Let’s create a new file in the models folder named “expression.go” with the following codes below:
package models
import "github.com/uadmin/uadmin"
// ---------------- DROP DOWN LIST ----------------
// Status ...
type Status int
// Keep ...
func (s Status) Keep() Status {
return 1
}
// DeletePrevious ...
func (s Status) DeletePrevious() Status {
return 2
}
// -----------------------------------------------
// Expression model ...
type Expression struct {
uadmin.Model
Name string `uadmin:"required"`
Status Status `uadmin:"required"`
}
// Save ...
func (e *Expression) Save() {
// If Status is equal to DeletePrevious(), it will delete
// the previous data in the list.
if e.Status == e.Status.DeletePrevious() {
uadmin.Delete(e) // <-- place it here
}
uadmin.Save(e)
}
Register your Expression model in the main function.
func main() {
// Some codes
uadmin.Register(
// Some registered models
models.Expression{}, // <-- place it here
)
// Some codes
}
Run the application. Go to the Expressions model and add at least 3 interjections, all Status set to “Keep”.
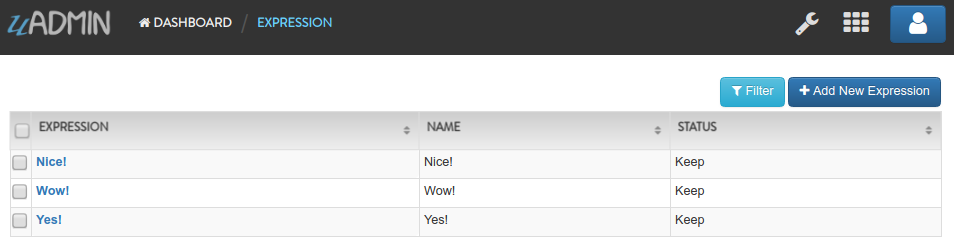
Now create another data, this time set the Status as “Delete Previous” and see what happens.
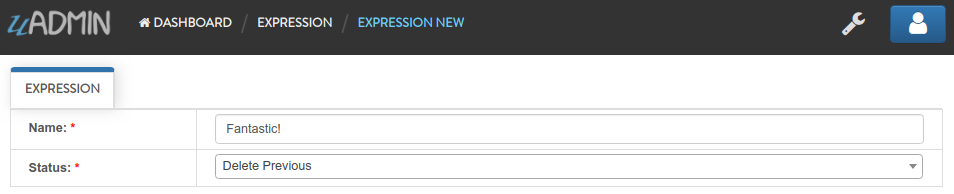
Result
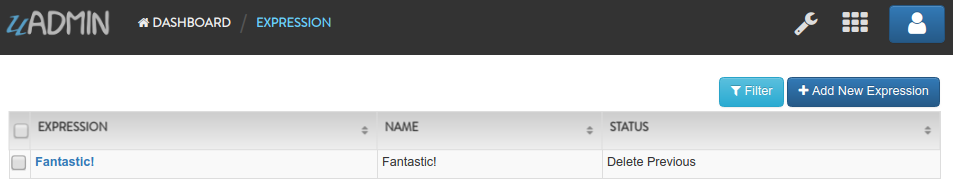
All previous records are deleted from the database.
Quiz:
uadmin.DeleteList¶
func DeleteList(a interface{}, query interface{}, args ...interface{}) (err error)
DeleteList deletes multiple records from database.
Parameters:
a interface{}: Is the variable where the model was initialized
query interface{}: Is an action that you want to perform in your database
args …interface{}: Is the series of arguments for query input
Before we proceed to the following examples, read Tutorial Part 9 - Introduction to API to familiarize how API works in uAdmin.
- Example #1: By Using API Handler (uadmin.DeleteList)
- Example #2: By Drop Down List Selection (uadmin.DeleteList)
Example #1: By Using API Handler (uadmin.DeleteList)¶
Suppose you have five records in your Todo model.

Create a file named delete_list.go inside the api folder with the following codes below:
// DeleteListHandler !
func DeleteListHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// r.URL.Path creates a new path called "/delete_list/"
r.URL.Path = strings.TrimPrefix(r.URL.Path, "/delete_list")
r.URL.Path = strings.TrimSuffix(r.URL.Path, "/")
// Call an array of Todo model
todo := []models.Todo{}
// Set the parameter as todo_id that can get multiple values
todoList := strings.Split(r.FormValue("todo_id"), ",")
// Delete the list of Todo records based on an assigned ID
uadmin.DeleteList(&todo, "id IN (?)", todoList)
}
Establish a connection in the main.go to the API by using http.HandleFunc. It should be placed after the uadmin.Register and before the StartServer.
func main() {
// Some codes
// DeleteListHandler
http.HandleFunc("/delete_list/", uadmin.Handler(api.DeleteListHandler)) // <-- place it here
}
api is the folder name while DeleteListHandler is the name of the function inside delete_list.go.
Run your application. Let’s assign 1, 2, and 3 in the todo_id parameter. (e.g. http://0.0.0.0:8080/delete_list/?todo_id=1,2,3).
Afterwards, go to Todo model and see what happens.
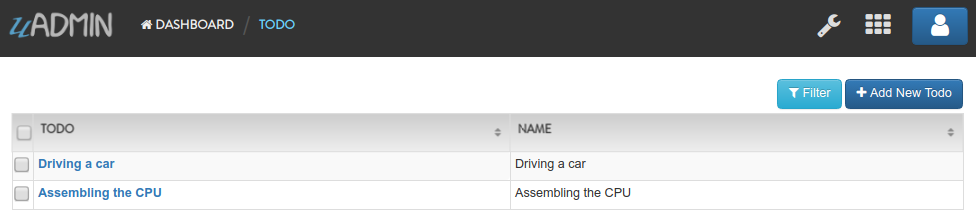
Based on the result shown above, the first three records are deleted from the database while the last two records remain.
Example #2: By Drop Down List Selection (uadmin.DeleteList)¶
Let’s create a new file in the models folder named “expression.go” with the following codes below:
package models
import "github.com/uadmin/uadmin"
// ---------------- DROP DOWN LIST ----------------
// Status ...
type Status int
// Keep ...
func (s Status) Keep() Status {
return 1
}
// Custom ...
func (s Status) Custom() Status {
return 2
}
// DeleteCustom ...
func (s Status) DeleteCustom() Status {
return 3
}
// -----------------------------------------------
// Expression model ...
type Expression struct {
uadmin.Model
Name string `uadmin:"required"`
Status Status `uadmin:"required"`
}
// Save ...
func (e *Expression) Save() {
// If Status is equal to DeleteCustom(), it will delete the
// list of data that contains Custom as the status.
if e.Status == e.Status.DeleteCustom() {
uadmin.DeleteList(e, "status = ?", 2)
}
uadmin.Save(e)
}
Register your Expression model in the main function.
func main() {
// Some codes
uadmin.Register(
// Some registered models
models.Expression{}, // <-- place it here
)
// Some codes
}
Run the application. Go to the Expressions model and add at least 3 interjections, one is set to “Keep” and the other two is set to “Custom”.
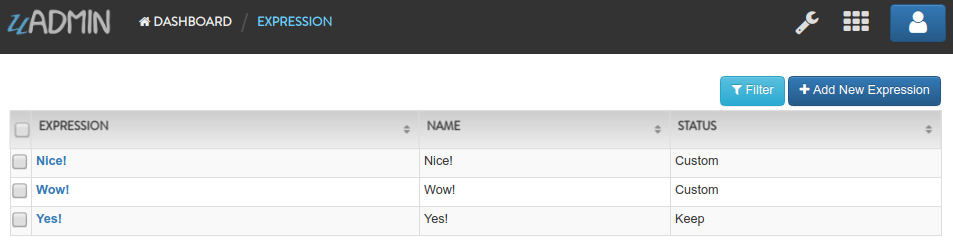
Now create another data, this time set the Status as “Delete Custom” and see what happens.
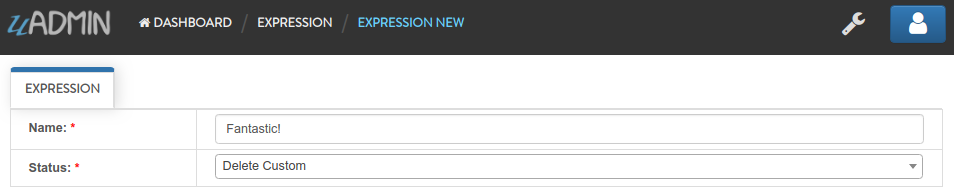
Result
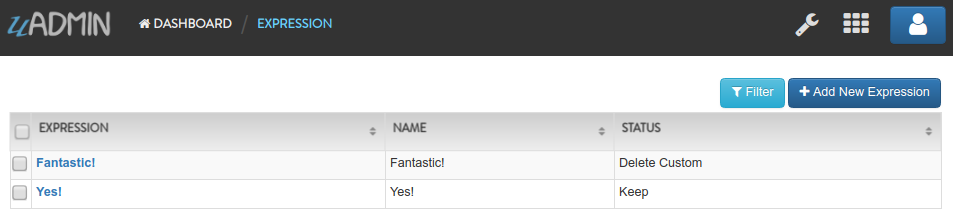
All custom records are deleted from the database.
Quiz:
uadmin.F¶
type F struct {
Name string
DisplayName string
ColumnName string
Type string
TypeName string
Value interface{}
Help string
Max interface{}
Min interface{}
Format string
DefaultValue string
Required bool
Pattern string
PatternMsg string
Hidden bool
ReadOnly string
Searchable bool
Filter bool
ListDisplay bool
FormDisplay bool
CategoricalFilter bool
Translations []translation
Choices []Choice
IsMethod bool
ErrMsg string
ProgressBar map[float64]string `json:"-"`
LimitChoicesTo func(interface{}, *User) []Choice `json:"-"`
UploadTo string
Encrypt bool
Approval bool
NewValue interface{}
OldValue interface{}
ChangedBy string
ChangeDate *time.Time
ApprovalAction ApprovalAction
ApprovalDate *time.Time
ApprovalBy string
ApprovalID uint
WebCam bool
Stringer bool
}
F is a field.
Parameters:
- Name - The name of the field
- DisplayName - The name that you want to display in the model. It is an alias name.
- ColumnName - The column name of the field
- Type - The field type (e.g. file, list, progress_bar)
- TypeName - The data type of the field (e.g. string, int, float64)
- Value - The value that you want to assign in a field
- Help - An instruction given to understand more details about the field or how to assign a value in a field
- Max - The maximum value the user can assign. It is applicable for numeric characters.
- Min - The minimum value the user can assign. It is applicable for numeric characters.
- Format - Implements formatted I/O with functions (e.g. %s - string, %d - Integer)
- DefaultValue - A value assigned automatically if you want to add a new record
- Required - A field that user must perform the given task(s). It cannot be skipped or left empty.
- Pattern - A regular expression
- PatternMsg - An error message if the user assigns a value that did not match the requested format
- Hidden - A feature to hide the component in the editing section of the form
- ReadOnly - A field that cannot be modified
- Searchable - A feature that allows the user to search for a field or column name
- Filter - A feature that allows the user to filter the record assigned in a model
- ListDisplay - A feature that will hide the field in the viewing section of the model if the value returns false
- FormDisplay - A feature that will hide the field in the editing section of the model if the value returns false
- CategoricalFilter - A feature that allows the user to filter the record assigned in a model in the form of combo box
- Translations - For multilingual fields
- Choices - A struct for the list of choices
- IsMethod - Check if the method should be included in the field list
- ErrMsg - An error message displayed beneath the input field
- ProgressBar - A feature used to measure the progress of the activity
- LimitChoicesTo - A feature used to append the fetched records in the drop down list
- UploadTo - A path where to save the uploaded files
- Encrypt - A feature used to encrypt the value in the database
- Approval - A feature used to set an approval permission in the field
- NewValue - A value that you want to replace from the old value
- OldValue - A value that was assigned before
- ChangedBy - Returns the username who changed the value of the field record
- ChangeDate - The date when the value of the field record was changed
- ApprovalAction - A selection of approval actions. There are two selections: Approved and Declined.
- ApprovalDate - The date when the value of the field record was approved
- ApprovalBy - Returns the username who approved the value of the field record
- ApprovalID - Returns the user ID who approved the value of the field record
- WebCam - A feature which adds web can access directly from the image and file fields
- Stringer - A feature that assigns a field as a unique type
func (F) MarshalJSON¶
func (f F) MarshalJSON() ([]byte, error)
MarshalJSON customizes F json export.
There are 2 ways you can do for initialization process using this function: one-by-one and by group.
One-by-one initialization:
func main(){
// Some codes
f := uadmin.F{}
f.Name = "Name"
f.DisplayName = "DisplayName"
f.ColumnName = "column_name"
f.Type = "Type"
f.Value = "Value"
}
By group initialization:
func main(){
// Some codes
f := uadmin.F{
Name: "Name",
DisplayName: "DisplayName",
ColumnName: "name",
Type: "Type",
Value: "Value",
}
}
In the following examples, we will use “by group” initialization process.
- Example #1: String Data Type
- Example #2: Progress Bar
- Example #3: Choices
- Example #4: Upload To
- Example #5: Approval
Page:
Quiz:
uadmin.ModelSchema¶
type ModelSchema struct {
Name string // Name of the Model e.g. OrderItem
DisplayName string // Display Name of the model e.g. Order Items
ModelName string // URL e.g. orderitem
TableName string // DB table name e.g. order_items
ModelID uint
Inlines []*ModelSchema
InlinesData []listData
Fields []F
IncludeFormJS []string
IncludeListJS []string
FormModifier func(*ModelSchema, interface{}, *User) `json:"-"`
ListModifier func(*ModelSchema, *User) (string, []interface{}) `json:"-"`
FormTheme string
ListTheme string
}
ModelSchema is a representation of a plan or theory in the form of an outline or model.
Here are the following fields and their definitions:
- Name - The name of the Model (e.g. OrderItem)
- DisplayName - A human readable version of the name of the Model (e.g. Order Items)
- ModelName - The same as the Name but in small letters for a URL (e.g. orderitem)
- TableName - The name for the database (e.g. order_items)
- ModelID - (Data) A place holder to store the primary key of a single row for form processing
- Inlines - A list of associated inlines to this model
- InlinesData - (Data) A place holder to store the data of the inlines
- Fields - A list of uadmin.F type representing the fields of the model
- IncludeFormJS - A list of string where you could add URLs to javascript files that uAdmin will run when a form view of this model is rendered
- IncludeListJS - A list of string where you could add URLs to javascript files that uAdmin will run when a list view of this model is rendered
- FormModifier - A function that you could pass that will allow you to modify the schema when rendering a form. It will pass to you the a pointer to the schema so you could modify it and a copy of the Model that is being rendered and the user access it to be able to customize per user (or per user group). Examples can be found in FM1, FM2.
- ListModifier - A function that you could pass that will allow you to modify the schema when rendering a list. It will pass to you the a pointer to the schema so you could modify it and the user access it to be able to customize per user (or per user group). Examples can be found in LM1, LM2.
- FormTheme - Name of the theme for the form
- ListTheme - Name of the theme for the list
func (ModelSchema) FieldByName¶
func (s ModelSchema) FieldByName(a string) *F
FieldByName returns a field from a ModelSchema by name or nil if it doen’t exist.
Structure:
modelschema.FieldByName("Name").XXXX = Value
XXXX has many things: See uadmin.F for the list. It is an alternative way of changing the feature of the field rather than using Tags. For more information, see Tag Reference.
func (*ModelSchema) GetFormTheme¶
func (s *ModelSchema) GetFormTheme() string
GetFormTheme returns the theme for this model or the global theme if there is no assigned theme for the model.
func (*ModelSchema) GetListTheme¶
func (s *ModelSchema) GetListTheme() string
GetListTheme returns the theme for this model or the global theme if there is no assigned theme for the model.
func (ModelSchema) MarshalJSON¶
func (s ModelSchema) MarshalJSON() ([]byte, error)
MarshalJSON customizes JSON export for models schema.
Used in the tutorial:
- Document System Tutorial Part 15 - Schema Form Modifier
- Document System Tutorial Part 16 - Schema List Modifier
There are 2 ways you can do for initialization process using this function: one-by-one and by group.
One-by-one initialization:
func main(){
// Some codes
modelschema := uadmin.ModelSchema{}
modelschema.Name = "Name"
modelschema.DisplayName = "Display Name"
}
By group initialization:
func main(){
// Some codes
modelschema := uadmin.ModelSchema{
Name: "Name",
DisplayName: "Display Name",
}
}
In the following examples, we will use “by group” initialization process.
- Example #1: IncludeFormJS
- Example #2: IncludeListJS
- Example #3: Fields
- Example #4: FormModifier and ListModifier
- Example #5: FormTheme and ListTheme
Page:
Quiz:
uadmin.Save¶
func Save(a interface{}) (err error)
Save saves the object in the database.
Parameter:
a interface{}: Is the model that you want to save with
Used in the tutorial:
- Document System Tutorial Part 9 - Updating the Document Version
- uAdmin Tutorial Part 5 - Register Inlines and Drop Down List
- uAdmin Tutorial Part 8 - Back-end Validation
- uAdmin Tutorial Part 11 - Inserting and Saving the Record
Let’s add an Invite field in the friend.go that will direct you to his website. In order to do that, set the field name as “Invite” with the tag “link”.
// Friend model ...
type Friend struct {
uadmin.Model
Name string
Email string
Password string
Nationality string
Invite string `uadmin:"link"`
}
To make it functional, add the overriding save function after the Friend struct.
// Save !
func (f *Friend) Save() {
f.Invite = "https://www.google.com/"
uadmin.Save(f) // <-- place it here
}
Run your application, go to the Friends model and update the elements inside. Afterwards, click the Invite button on the output structure and see what happens.
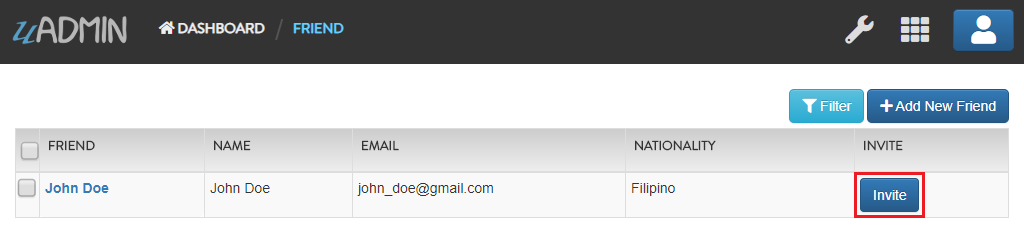
Result

Quiz:
uadmin.Schema¶
var Schema map[string]ModelSchema
Schema is the global schema of the system.
Used in the tutorial:
Examples:
- Approval
- CategoricalFilter
- Choices
- DefaultValue
- DisplayName
- Encrypt
- ErrMsg
- Filter
- FormDisplay
- Help
- Hidden
- ListDisplay
- Max
- Min
- Pattern
- PatternMsg
- ProgressBar
- ReadOnly
- Required
- Stringer
- Type
- UploadTo
- WebCam
Page:
Quiz:
uadmin.Update¶
func Update(a interface{}, fieldName string, value interface{}, query string, args ...interface{}) (err error)
Update updates the field name and value of an interface.
Parameters:
a interface{}: Is the variable where the model was initialized
fieldName string: Is the field name that you want to access to
value interface{}: Is the value that you want to update in the field
query string: Is the command you want to execute in the database
args …interface{}: Is the series of arguments that you want to update in the query
Suppose you have one record in your Todo model.
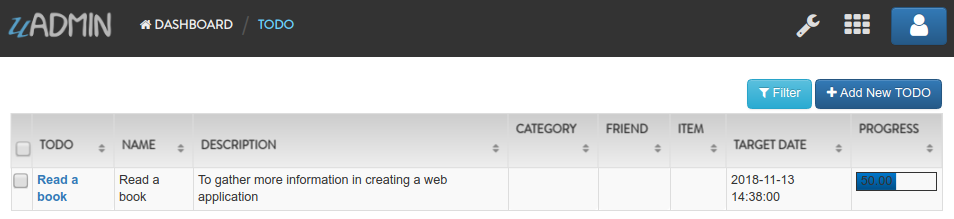
Go to the main.go and apply the following codes below:
func main(){
// Some codes
// Initialize todo and id
todo := models.Todo{}
id := 1
// Updates the Todo name
uadmin.Update(&todo, "Name", "Read a magazine", "id = ?", id)
}
Now run your application, go to the Todo model and see what happens.
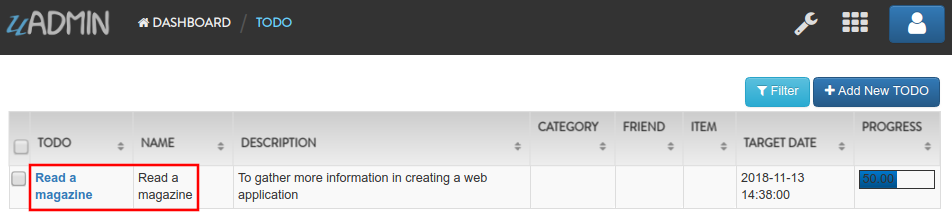
The Todo name has updated from “Read a book” to “Read a magazine”.
Quiz: